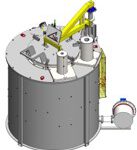
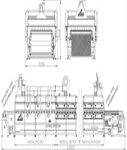
Furnaces used to provide heat for an industrial process and can serve as reactor which provides heats of reaction. In TAD, Furnace designs vary as to its function, heating duty, type of fuel and method of introducing combustion air.
Here are some categories:
►Oven Atmosphere:
•Normally oxidizing
•under protective gas (inert or reducing)
►Warming Material:
•Metals (rods, bolts, sheets, ingots, cast & molded parts)
•Non-metals (plastics, ceramics, glass, filter materials, etc.)
•Bulk material (e.g. activated carbon)
►Design/Type:
•Continuous ovens (belt, chain, belt & roller transport)
•Chamber & retort furnaces
•Rotary hearth & rotary kiln systems
►Heat Transfer Through:
•Convection & high convection (air circulation)
•Radiation
►Heating Type:
•Gas heated (natural gas or propane)
•Electrically heated
•Hybrid heated (combination of gas & electric heating)
►Process/Procedure:
•Drying & Curing
•Hardening & Tempering
•Annealing (various processes)
•Nitriding
•Heating & cooling (direct and indirect)
►Periphery:
•Transportation peripherals (conveyors, feeding and removal devices)